 In the past 10 years, bed bugs have begun making a comeback across the United States. Their diet consists only of blood. Bed Bugs feed like mosquitoes by extracting blood from their meal source whether it is humans, animals or birds. They are totally incapable of eating food like
In the past 10 years, bed bugs have begun making a comeback across the United States. Their diet consists only of blood. Bed Bugs feed like mosquitoes by extracting blood from their meal source whether it is humans, animals or birds. They are totally incapable of eating food like
other insects or mammals. Ant and roach baits have no impact. Aerosol bombs for fleas or other insects don’t work either other than making the bugs scatter to different areas of the same room or to adjacent rooms. International travel and commerce have facilitated the spread of these insect hitchhikers that have been found on airplanes, ships, trains and buses.
Bed bugs are most frequently found in dwellings with a high rate of occupant turnover. Hotels and motels certainly fall into that category along with college dormitories and apartment complexes to just mention a few.
Eradicating bed bugs is more difficult and more costly than dealing with other types of pests. Residents inadvertently bring bed bugs home with them when they go away for vacation and/or business. Moving from one apartment community to another can also help spread the problem. Traditional pest control methods, which emphasize the routine application of pesticides often
ignore the root causes of infestations, allowing bed bug populations to persist.
 Effective management and treatment involves the commitment of both the resident and landlord. An Integrated Pest Management Plan promotes the prevention of infestation through education, inspection, and other preventative measures. Consistent information to both landlord and tenant, early detection, and application of treatment to targeted sites, will help prevent spreading the problem, make for happier tenants and a better “bottom line.”
Effective management and treatment involves the commitment of both the resident and landlord. An Integrated Pest Management Plan promotes the prevention of infestation through education, inspection, and other preventative measures. Consistent information to both landlord and tenant, early detection, and application of treatment to targeted sites, will help prevent spreading the problem, make for happier tenants and a better “bottom line.”


 Worst Bed Bug City” is an award that nobody will show up to receive. But while bed bugs are active in all 50 states, some urban areas see more infestations per year than others. Let’s look at the cities that are the unlucky winners for 2019:
Worst Bed Bug City” is an award that nobody will show up to receive. But while bed bugs are active in all 50 states, some urban areas see more infestations per year than others. Let’s look at the cities that are the unlucky winners for 2019: Research supports the view that total-release foggers lack the ability to penetrate into typical harborages used by many household insects, therefore rendering these products ineffective as control agents.
Research supports the view that total-release foggers lack the ability to penetrate into typical harborages used by many household insects, therefore rendering these products ineffective as control agents.


 The common bedbug is an insect that feeds on human blood. They are often foun
The common bedbug is an insect that feeds on human blood. They are often foun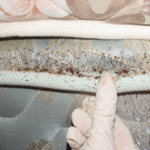
 Places of business are generally not ideal for bed bug infestations to become established because there is little opportunity for the bugs to feed on sleeping or stationary persons.
Places of business are generally not ideal for bed bug infestations to become established because there is little opportunity for the bugs to feed on sleeping or stationary persons.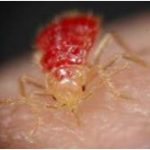 When temperatures drop, many of the bugs that bite or sting us like fleas go into a sort of hibernation mode. So, it makes sense to ask whether or not bed bugs do the same. But the way bugs hibernate isn’t the same as the way many animals hibernate. Bugs go into a low-energy state called diapause, just like it sounds, it’s a state of pause in their development.
When temperatures drop, many of the bugs that bite or sting us like fleas go into a sort of hibernation mode. So, it makes sense to ask whether or not bed bugs do the same. But the way bugs hibernate isn’t the same as the way many animals hibernate. Bugs go into a low-energy state called diapause, just like it sounds, it’s a state of pause in their development.
 Early detection and prompt, effective action is critical to prevent bed bugs from becoming established in an apartment building or buildings. Once established, bed bugs are among the most difficult and expensive pests to control. Success demands aggressive action and perseverance in tracking down and eliminating every last bug.
Early detection and prompt, effective action is critical to prevent bed bugs from becoming established in an apartment building or buildings. Once established, bed bugs are among the most difficult and expensive pests to control. Success demands aggressive action and perseverance in tracking down and eliminating every last bug.
 spend time resting.
spend time resting.